09. 布尔表达式
原创2025/5/29...大约 3 分钟
1. 条件判断(布尔值)
temperature = 30
is_hot = temperature > 25
print(f'Is it hot? {is_hot}')
weather = 'sunny'
is_sunny = (weather == 'sunny')
print(f'Is it sunny? {is_sunny}')
should_go_swimming = is_hot and is_sunny
print(f'Should go swimming? {should_go_swimming}')
#-------output-------
Is it hot? True
Is it sunny? True
Should go swimming? True2. 布尔运算中的空
在判断时,需要注意:
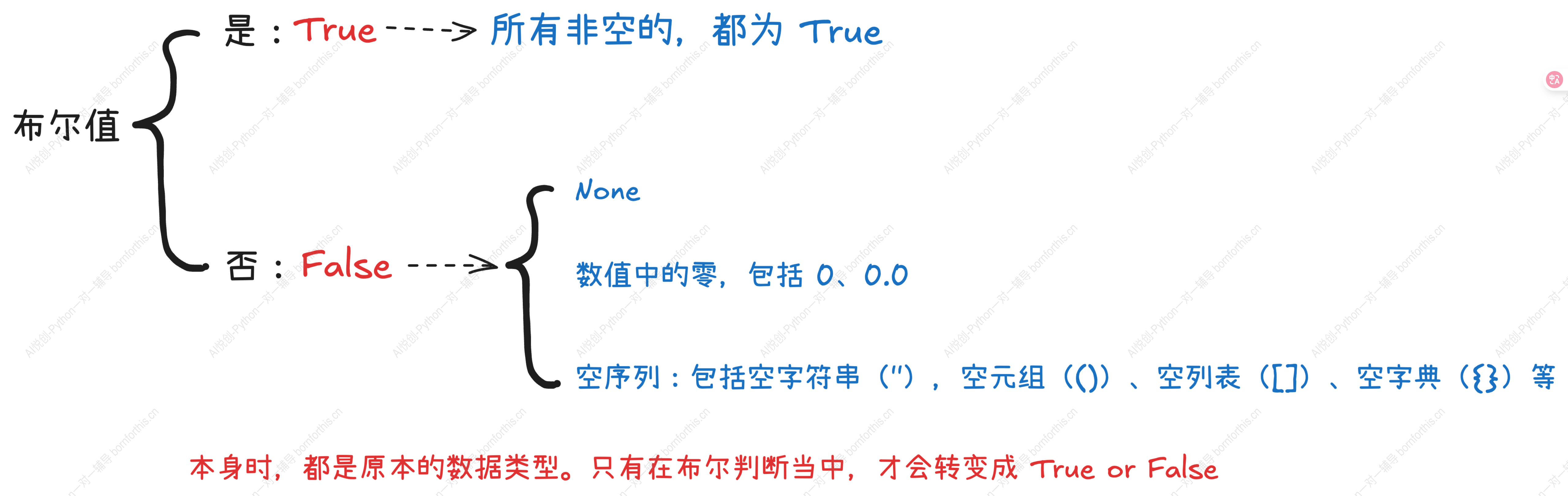
示例如下:
# 当做正常变量使用时,虽然数据是空的,但是都是原本的数据类型
string = ''
dictionary = {}
lst = []
tup = ()
set_1 = set()
print(f'空字符串:"{string}", type: {type(string)}')
print(f'空字典:{dictionary}, type: {type(dictionary)}')
print(f'空列表:{lst}, type: {type(lst)}')
print(f'空元组:{tup}, type: {type(tup)}')
print(f'空集合:{set_1}, type: {type(set_1)}')
# 只有在布尔运算或者强制转换中,空序列等都会得到 False:
# 以下为空数据结构通过 bool() 转换后的类型和值
string = bool('')
print(f"'' → type: {type(string)}, value: {string}")
dictionary = bool({})
print(f"{{}} → type: {type(dictionary)}, value: {dictionary}")
lst = bool([])
print(f'[] → type: {type(lst)}, value: {lst}')
tup = bool(())
print(f'() → type: {type(tup)}, value: {tup}')
set_1 = bool(set())
print(f'set() → type: {type(set_1)}, value: {set_1}')
#-------output-------
空字符串:"", type: <class 'str'>
空字典:{}, type: <class 'dict'>
空列表:[], type: <class 'list'>
空元组:(), type: <class 'tuple'>
空集合:set(), type: <class 'set'>
'' → type: <class 'bool'>, value: False
{} → type: <class 'bool'>, value: False
[] → type: <class 'bool'>, value: False
() → type: <class 'bool'>, value: False
set() → type: <class 'bool'>, value: False3. 逻辑运算符
逻辑运算只存在于布尔类型中。
and 逻辑 “与”,当运算符两边的运算对象都为 True 时,结果为 True;
or 逻辑“或”,当运算符两边的运算对象的其中一个为 True 时,结果为 True;
not 逻辑“非”,用于反转运算对象的状态(一个运算对象即可)。
In [1]: not False
Out[1]: True
In [2]: not True
Out[2]: False
In [3]: not False and True or False
Out[3]: True
In [4]: not True or not False
Out[4]: True
In [5]: not True or False and True
Out[5]: False
In [6]: (not False and True) or False
Out[6]: True
In [7]: not (True or False) and (False or True)
Out[7]: False
In [8]: not (True and False) and (False or True)
Out[8]: True- 逻辑运算符的优先级:not 优先于 and, 而 and 又高于 or。
- 短路求值:在 and 中,如果左侧为 False ,右侧不会被求值;在 or 中,如果左侧为 True,则右侧不会被求值。
- 通过加括号可以明确表达式的求值顺序,从而使代码更易读、更不容易出错。
4. 运算结果与短路求值
| 3 and 5 | True and True | True | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 or 5 | True or True | True | 3 |
| 0 or 5 | False or True | True | 5 |
| 3 and not 5 | True and False | False | 返回值为空 |
短路求值:
# 如何证明出现了短路求值
# 运行了 10/0 时会报错
# print(10/0)
print(True or (10/0))
#-------output-------
Truecondition = False or print('我被执行了!')
print(condition)
#-------output-------
我被执行了!
None # 因为 print('我被执行了!') 是执行代码,没有返回值,所以 condition 输出了 None5. 表达式应用——条件测试
在编程中,表达式常用于条件测试,帮助我们根据不同情况执行不同代码。常见应用场景包括:
- 比较操作:检查一个变量是否等于或不等于某个特定值,或比较两个数字的大小。
- 成员资格测试:判断一个特定值是否存在于某个序列(如列表、字符串、元组)中。
5.1 使用 and 检查多个条件
age_lilei = 17
age_hanmeimei = 18
result1 = age_lilei >= 18 and age_hanmeimei >= 18
print(result1)
result2 = age_lilei >= 15 and age_hanmeimei >= 15
print(result2)
#-------output-------
False
True5.2 使用 or 检查多个条件
age_lilei = 17
age_hanmeimei = 18
result1 = age_lilei >= 18 or age_hanmeimei >= 15
print(result1)
result2 = age_lilei >= 20 or age_hanmeimei >= 20
print(result2)
#-------output-------
True
False更新日志
2025/5/29 08:02
查看所有更新日志
9d836-于
